CASA BLOGS
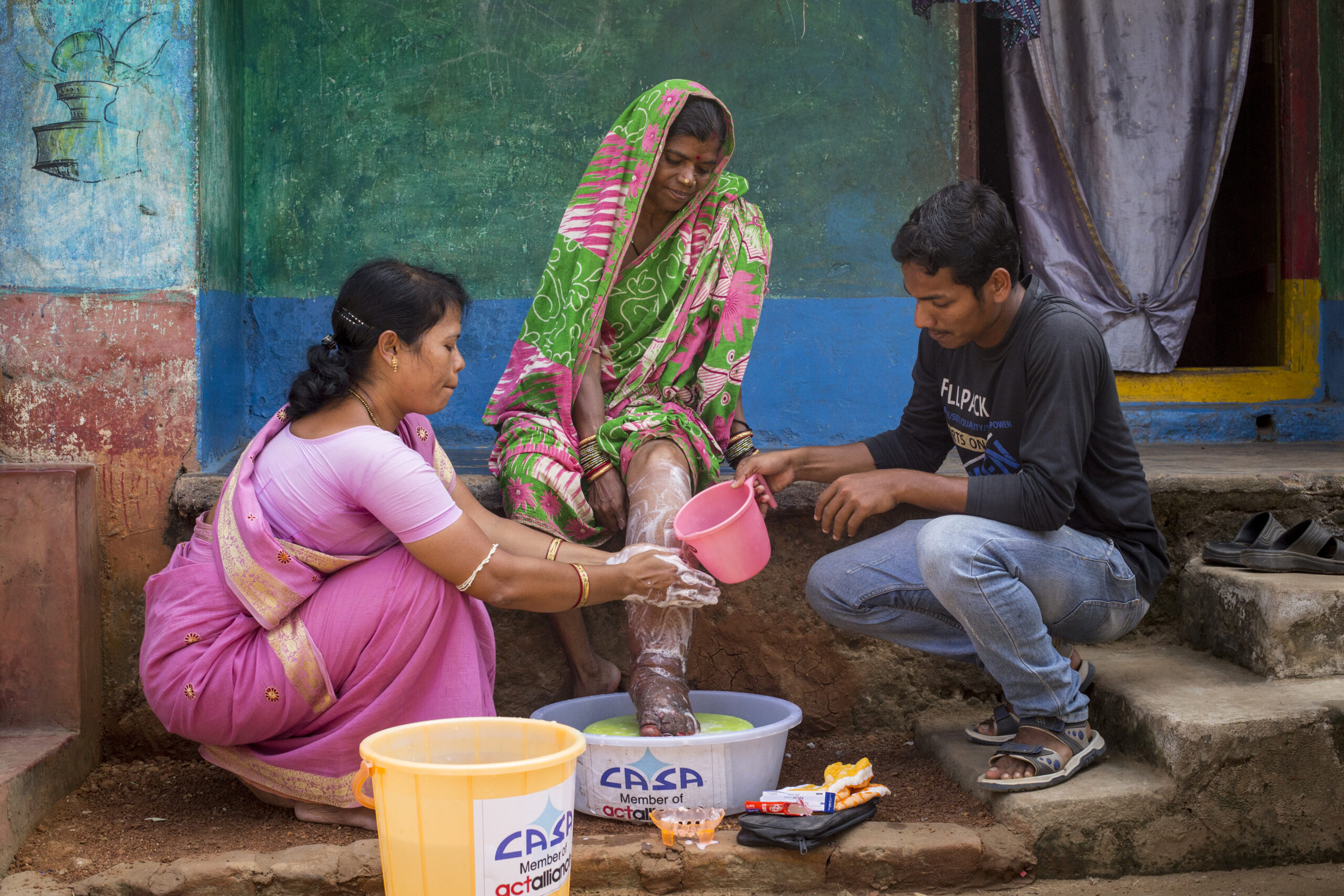
Eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis: A Comprehensive Approach for Society
Introduction
Lymphatic filariasis (LF), also known as elephantiasis, is a debilitating neglected tropical disease affecting millions of individuals worldwide. This parasitic infection is caused by thread-like worms transmitted through mosquito bites, resulting in chronic lymphatic dysfunction, disfigurement, and severe disability. To eradicate LF from society, a multi-pronged approach is necessary, including preventive measures, treatment strategies, community engagement, and education. This article outlines key steps for eliminating lymphatic filariasis and creating a society free from its burden.
Enhanced Surveillance and Early Detection:
1. Implementing an effective surveillance system is crucial to identify LF-endemic areas and track disease prevalence. This can be achieved by strengthening the capacity of local health systems to conduct surveys, perform diagnostic tests, and report cases. Early detection of infected individuals allows for timely interventions and prevents disease progression. Collaborations with healthcare providers, laboratories, and community health workers play a pivotal role in achieving this goal.
Vector Control:
2. Controlling the mosquito vectors that transmit LF is vital for preventing new infections. Integrated vector management strategies should be employed, including the use of insecticide-treated bed nets, indoor residual spraying, larviciding, and environmental management. Community involvement is essential in promoting the use of these interventions, ensuring their proper application, and raising awareness about vector control measures.
Mass Drug Administration:
3. Mass drug administration (MDA) involves distributing antiparasitic medications to entire populations in endemic areas, even if individuals are not currently infected. Two drugs, albendazole and ivermectin, are commonly used for eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis treatment. MDA aims to interrupt transmission by reducing the number of parasites in the community. It is crucial to ensure high treatment coverage and compliance to achieve the desired impact. Close collaboration with community leaders, local health workers, and volunteer organizations like CASA can increase participation and acceptance of MDA programs.
Access to Healthcare and Treatment:
4. Improving access to healthcare services and treatment is essential for individuals affected by LF. This includes establishing specialized LF clinics, training healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care, and ensuring the availability of necessary medications and supplies. Integration of LF services into existing healthcare systems enhances efficiency and facilitates timely diagnosis, treatment, and management of LF-related complications.
Health Education and Community Engagement:
5. Community engagement and health education programs play a crucial role in preventing LF transmission and reducing stigma associated with the disease. Educational initiatives should focus on raising awareness about LF transmission, symptoms, prevention methods, and available treatments. Empowering communities with knowledge allows them to take ownership of their health and actively participate in disease prevention efforts.
6. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Interventions: Improving water, sanitation, and hygiene conditions can contribute to the prevention and control of eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis. Access to clean water, proper sanitation facilities, and hygiene education can minimize the breeding sites of mosquito vectors, reduce exposure to contaminated water sources, and promote personal hygiene practices. Implementing WASH interventions in endemic areas complements other preventive measures and enhances the overall impact of LF elimination efforts.
7. Disability Management and Rehabilitation: Addressing the needs of individuals already affected by LF is crucial for their well-being and reintegration into society. Establishing disability management and rehabilitation programs can provide specialized care, including physiotherapy, wound care, and psychosocial support. These programs aim to improve the quality of life for those living with LF-related disabilities and reduce the social stigma associated with the disease.
8. Research and Innovation: Continued research and innovation are essential for developing new tools, strategies, and interventions to accelerate LF elimination. Investing in research can lead to the discovery of more effective drug treatments, improved diagnostic methods, and innovative vector control measures. Collaborative partnerships between researchers, policymakers, and communities can foster innovation and ensure the implementation of evidence-based approaches in LF control programs.
9. Cross-Sector Collaboration: Eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis requires collaboration across various sectors, including health, education, agriculture, and infrastructure development. Engaging governmental agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), private sectors, and international partners in a coordinated effort can pool resources, expertise, and infrastructure to address the multiple facets of LF elimination. Cross-sector collaboration fosters synergy, maximizes impact, and promotes sustainable solutions for long-term success.
10. Monitoring, Evaluation, and Data Management: Establishing robust monitoring, evaluation, and data management systems are essential for assessing the progress and impact of LF elimination efforts. Regular monitoring and evaluation allow for timely identification of challenges, identification of gaps, and adjustment of strategies accordingly. Collecting accurate and comprehensive data enables evidence-based decision-making, resource allocation, and targeted interventions.
Conclusion:
Eliminating lymphatic filariasis from society requires a comprehensive and multi-dimensional approach. Enhanced surveillance, early detection, vector control, mass drug administration, improved access to healthcare, and health education are key strategies that, when implemented collectively, can effectively combat the disease. Collaboration between governments, healthcare systems, NGOs, and communities is vital for successful LF elimination efforts. By working together, we can create a society free from the burden of lymphatic filariasis, promoting the well-being and productivity of affected individuals and communities worldwide.
 Previous Blog Post Importance of engaging community during disaster risk management with NGOs
Previous Blog Post Importance of engaging community during disaster risk management with NGOsFeatured Post

Empowering Rural Education in India:
14 Mar 2024
Introduction: In the vast tapestry of India, education is the key to unlocking the door to a brighter future. However, the challenge of providing quality education to the rural parts of the country persists. In this blog post, we will delve into the crucial role that Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) play in bridging the educational gap […]

Empowering the Future: Disaster Management Training for School Children in Disaster-Prone Areas
22 Feb 2024
Introduction: In the face of increasing natural disasters worldwide, it becomes imperative to equip our younger generation with the knowledge and skills necessary to handle emergency situations. Children, being one of the most vulnerable groups during disasters, can greatly benefit from disaster management training. This blog explores the significance of imparting such training, with a […]

Empowering Women: Transforming Lives Through Sustainable Livelihoods in Rural India
16 Feb 2024
Introduction: In the heart of rural India, a silent revolution is taking place as women embrace newfound opportunities for sustainable livelihoods. This transformation not only uplifts individual lives but also contributes to the overall development of communities. At [Your Organization’s Name], we are committed to driving positive change by providing women in rural India with […]


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.